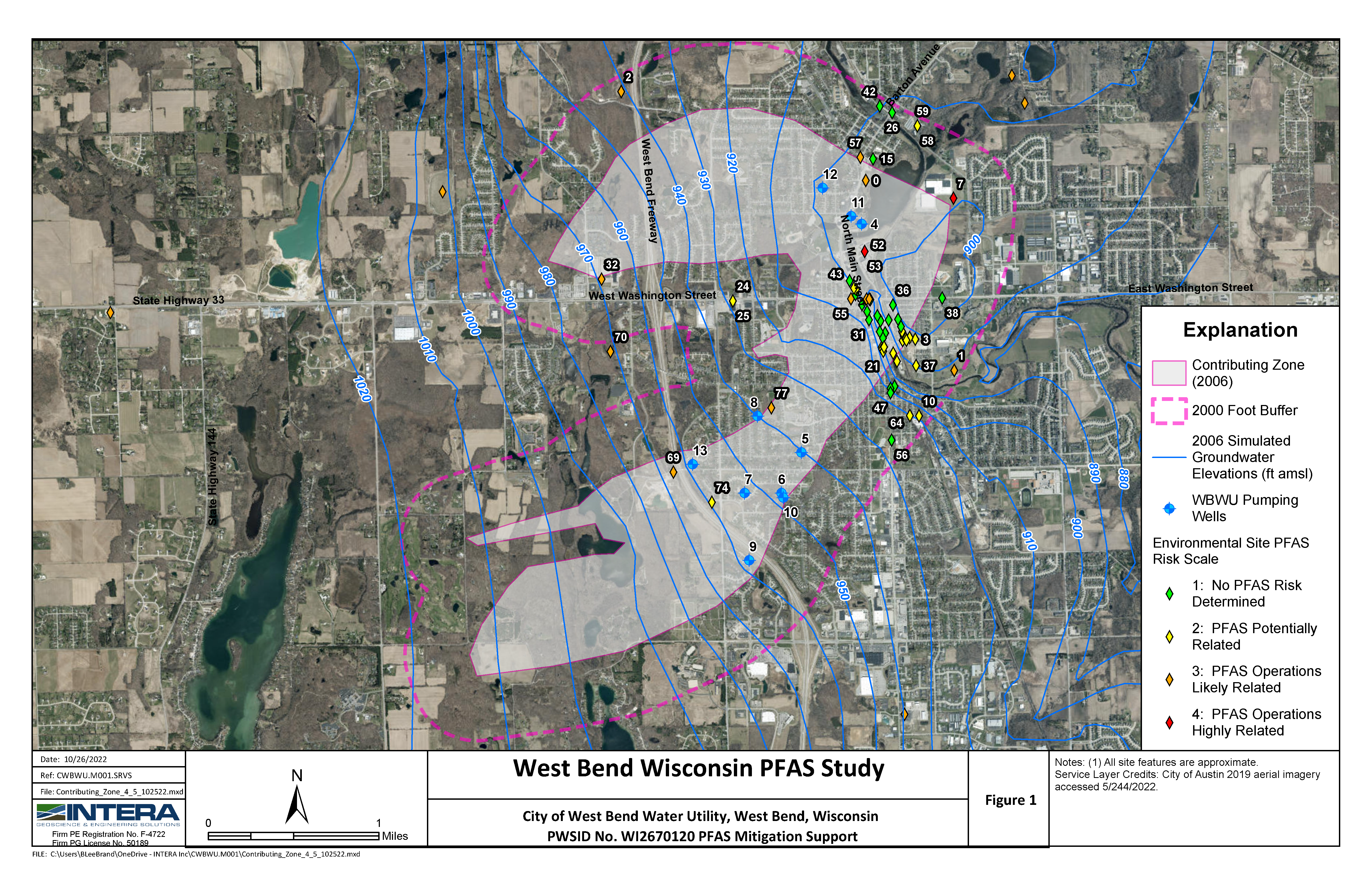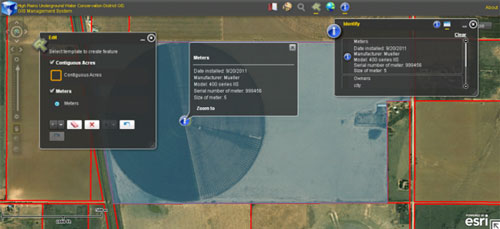
Challenge. Develop a more automated system to enable water well owners and operators to report well locations, meter locations, and meter readings
Solution. The High Plains Underground Water Conservation District (HPWD) is the largest and oldest of the Texas conservation districts, and oversees approximately 1.7 million irrigated acres. Rule changes motivated HPWD to develop a more automated system for allowing water well owners and operators to report well locations, meter locations, meter readings, the association between meters and wells, and contiguous acres. To address this need, INTERA developed a web-based system that includes user accounts so that information can be managed on an individual operator basis. Once logged in, an operator uses a map-based system, complete with cache-based imagery, to indicate which properties they are farming. The operator can then use a meter tool to enter the location of the water meters (or alternative methods) that are being used to track water production. A second tool allows the operator to show which wells are connected to each meter, and the mapping tool shows those associations in real-time. Once the meters have been entered into the geodatabase via the mapping tool, the operator can select any meter and report readings to help manage water use. Additional tools allow the operator to indicate missing wells (i.e., wells that are active on the property, but missing from HPWD records, and hence, do not appear on the map). These web-based tools allow operators to easily self-report information to HPWD, reducing the District staff workload. The technology behind this system includes ESRI ArcGIS Server running on a virtual Windows Server installation through Amazon EC2, a cloud-computing system. The cloud-based system allows superior uptime, bandwidth, and ease of maintenance compared to a local server, in cases where local resources do not include significant IT infrastructure. Both the HPWD relational database (containing all district data on wells, water levels, etc.) and the geodatabase (containing feature classes with location information specific to GIS tasks) reside in a Microsoft SQL server database structure. On the client side, the web account system was developed in ASP.NET MVC, using a look and feel that integrates seamlessly into the current HPWD website. The client-side mapping system and tools were developed on the foundation of FlexViewer, and communication between the client and server side is accomplished through ArcSDE and custom APIs.