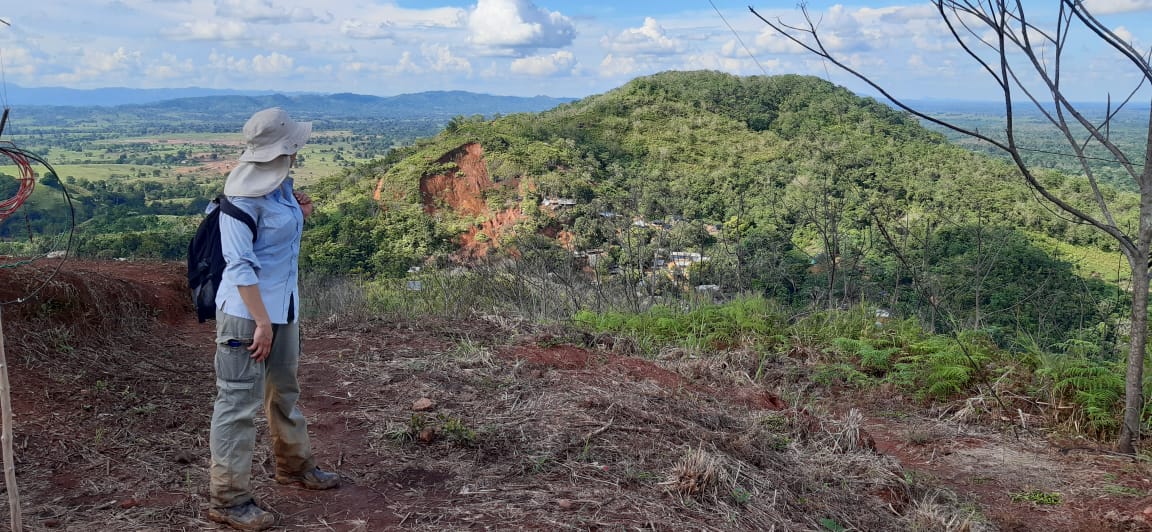
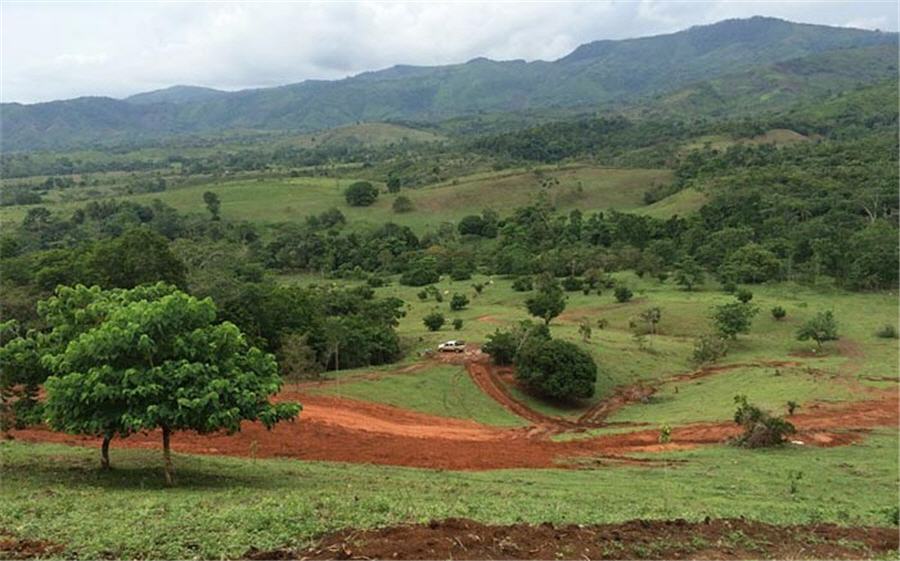
Challenge: To develop and implement a baseline geochemical, hydrogeologic and hydrologic program for permitting of a proposed Cu-Ag-Au open pit mine in a remote area with limited road access, three meters of annual rainfall, and artisanal mining impacts.
Solution: INTERA, in collaboration with our national partner Servicios Hidrogeológicos Integrales, designed and performed baseline evaluations of site hydrogeology, hydrology, sediment chemistry and mine waste geochemistry. The baseline study included: 1) characterization of the surface water within the hydrologic “area of influence” 2) design and oversite of an aquifer characterization program using a variety of tests (packer, injection, slug and pumping) and well test data interpretation using nSIGHTS,(3) design, and implementation of surface water and groundwater monitoring program, including automated stream gaging stations; 4) development and implementation of geochemical characterization programs for waste rock, tailings, ore, pit walls and soils using static and kinetic testing (humidity cells and barrels), including characterization and evaluation of extent/volume of artisanal tailings deposited in streams , 5) groundwater modeling to determine the number and location of dewatering wells and impacts of pit dewatering, 6) pit lake and process water geochemical modeling to inform water treatment alternatives and discharge mixing models, 7) development and geochemical modeling of a mine waste co-disposal facility (in collaboration with Knight Piesóld), and 8) precipitation analysis and calculation of site specific intensity/duration/frequency. This last task required a high degree of data manipulation and infilling due to the varying recording periods and elevations of the stations, and data gaps.
Results: Data from the baseline studies were consolidated into a series of reports, including the Mine Permit application (Plan de Trabajos y Obras [PTO]), PFS and FS NI 43-101 Technical Reports, and the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). Patrick Williamson of INTERA was the QP for Section 20 of the Technical Reports.